 Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina
More detailed report: National Policy Report
National coordinator: Nermina KATKIC

 CULTURAL HERITAGE POLICY
CULTURAL HERITAGE POLICY
The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina (Dayton Peace Agreement) defines the role of the different administrative levels (Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Republika Srpska and the Brčko District) regarding the heritage as well as it underlines the importance of its restorationwithin the peace process.
Annex 8, Article 6 of the General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina provides a definition of what is eligible to be designated as a national monument: movable or immovable property of great importance to a group of people with common cultural, historic, religious or ethnic heritage, such as monuments of architecture, art or history; archaeological sites; groups of buildings; as well as cemeteries.
Annex 8 also introduces to the legal system a definition of the term “rehabilitation” – restoration to its condition prior to destruction of a property damaged or destroyed during the 1992-1995 war.
 INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK
INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK
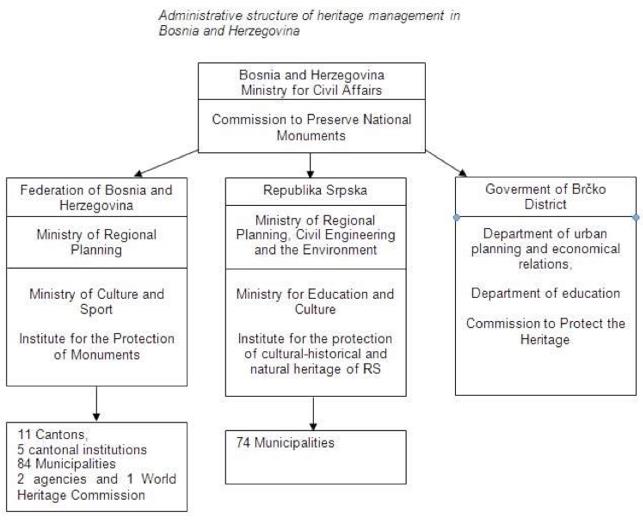
Commission to Preserve National Monuments
At the national level, Commission to Preserve National Monuments (hereinafter: the Commission) is the INSTITUTION of Bosnia and Herzegovina responsible for both the heritage protection and the international cooperation in the field. It is set up by the General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Decision of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina on the Commission to Preserve National Monuments. Pursuant to the powers conferred on it by Annex 8 of the General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Commission issues decisions designating movable and immovable properties as national monuments, applying the Criteria for the designation of properties as national monuments. Also, it is responsible for concluding international agreements. Thus, it takes charge of the drafting and execution of the agreements; it takes part in the negotiations as a specialist.
Ministry of Civil Affairs
Pursuant to the Law on Ministries and Other Administrative Organs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Ministry of Civil Affairs is responsible for prescribing the basic principles of the coordination of activities, harmonizing the plans of the entity authorities and defining strategy at the international level in the field of, inter alia, the culture, the sciences and the education.
Regional governments
At subnational level, the Commission’s decisions lie with the regional governments and the Ministries responsible for regional planning and for culture. The Governments of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Republika Srpska and Brcko District are responsible for providing the legal, scientific, technical, administrative and financial measures for the protection, conservation, restoration and presentation of national monuments.
The governments provide the resources to develop the technical documentation required for both the restoration of national monuments and the implementation of its provisions. The subnational institutions responsible for the protection of the cultural, historical and natural heritage are funded by entity budgets via the entity ministries responsible for culture. Also, the relevant ministries of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Republika Srpska and Brcko District ensure funds for work on monuments, including endangered national monuments, independently of their ownership (public-private).
Cantonal level
At the cantonal level, Five of the eleven cantons have their own cantonal institutes: Sarajevo, Tuzla, Bihac, Bugojno and Mostar.
Other institutions
Finally, the heritage protection institutions provide both specialized know-how and supervision to restoration projects. They are also responsible for the implementation of projects funded by the entity governments and for the protection of properties not designated national monuments.
 LEGAL FRAMEWORK
LEGAL FRAMEWORK
Main reference texts concerning heritage protection law:
- The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina (Dayton Peace Agreement), Annex 8 – Agreement on the Commission to Preserve National Monuments; 1995.
- The Decision of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina on the Commission to Preserve National Monuments, 2001
- The Rules on the Activities of the Commission to Preserve National Monuments with respect to International Co-operation, 2002
- The Criteria for the Designation of Property as National Monuments, 2002/2003
- The Law on the Implementation of Decisions of the Commission to Preserve National Monuments Established Pursuant to Appendix 8 of the Dayton Agreement, 2002, adopted by the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- The Law on the Implementation of Decisions of the Commission to Preserve National Monuments Established Pursuant to Appendix 8 of the Dayton Agreement, 2002, adopted by the Republika Srpska
- The Law on the Implementation of Decisions of the Commission to Preserve National Monuments Established Pursuant to Appendix 8 of the Dayton Agreement, 2002, adopted by the District of Brčko
- The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina Law on Regional Planning and Land Use,
- The Republika Srpska Law on Regional Planning, consolidated text
- The Brcko District Law on Regional Planning
- The Criminal Code of Republika Srpska, Articles 253 and 254
- The Criminal Code of the Federation of BiH, Articles 321 and 322
- The Criminal Code of Brčko District BiH
- The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina Law on the Protection of Nature
- The Republika Srpska Law on the Protection of Nature
- The Brčko District Law on the Protection of Nature
- The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina Law on the Protection of the Environment
- The Republika Srpska Law on the Protection of the Environment
- The Brčko District Law on the Protection of the Environment
- The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina Law on Inspection.
Other laws currently in force:
- In Republika Srpska: the Law on Cultural Property, 1995, and the Law on Amendments to the Law on Cultural Property
- In the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina: the Law on the Protection and Preservation of the Cultural, Historical and Natural Heritage, of 1985, as amended in 1987, 1993 and 1994, in force and implemented in the cantons that do not have their own laws: Posavski (Sava Valley) Canton, Tuzla Canton, Bosnia-Podrinjski (Drina Valley) Canton, Central Bosnia Canton and Herceg-Bosna Canton
- Cantons that have enacted heritage laws: Sarajevo Canton – Law on the Protection of the Cultural Heritage; West Herzegovina Canton – Law on the Protection and Use of the Cultural, Historical and Natural Heritage; Zenica Doboj Canton – Law on the Protection of the Cultural Heritage; Herzegovina Neretva Canton – Law on the Protection of the Cultural Heritage in Herzegovina Neretva Canton and Law on Building Permits Beyond the Boundaries of National Monuments or Interim Boundaries and Implementation of Protection measures; Una Sana Canton – Law on the Protection of the Cultural Heritage.
 RATIFIED INTERNATIONAL CONVENTIONS
RATIFIED INTERNATIONAL CONVENTIONS
Council of Europe
- European Cultural Convention (Council of Europe, Paris, 1954)
- European Convention on the Protection of the Archaeological Heritage (Council of Europe, London, 1969)
- Convention for the Protection of the Architectural Heritage of Europe (Council of Europe, Granada, 1985)
- European Convention on the Protection of the Archaeological Heritage, revised (Council of Europe, Valletta, 1992)
- Framework Convention on the Value of Cultural Heritage for Society (Council of Europe, Faro, 2005).
- European Landscape Convention (Council of Europe, Florence, 2000)
- Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (UNESCO, Paris, 1972)
Unesco
- Convention on the Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Import, Export and Transfer of Ownership of Cultural Property (UNESCO, Paris, 1970)
- Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict (UNESCO, The Hague, 1954)
- Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage (UNESCO, Paris, 2003)
- Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage (UNESCO, Paris, 2001)
- Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions (UNESCO, Paris, 2005)
- Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage (UNESCO, Paris, 2003)



