Ireland
STRUCTURE OF THE NATIONAL EDUCATION SYSTEM
 Source: Eurydice 2022/23
Source: Eurydice 2022/23
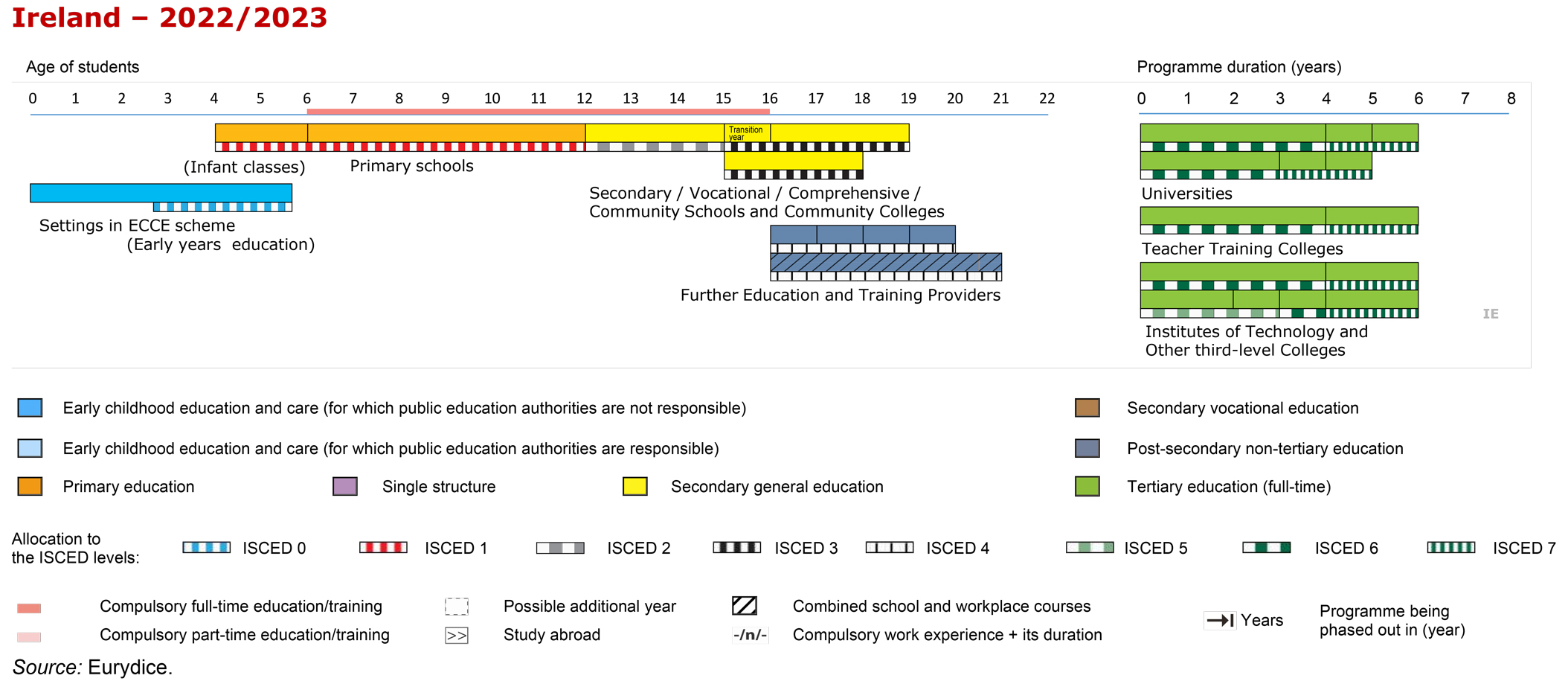
The education system in Ireland consists of three levels: early years, primary and post-primary education.
Education is compulsory for children in Ireland from the ages of 6 to 16 or until students have completed three years of post-primary education. In Ireland, the majority of primary and secondary schools are publicly funded. A minority of students are educated in private schools or through home tuition. Primary education consists of an eight-year cycle and students follow a national curriculum.
There are three types of secondary schools (voluntary secondary, Education and Training Board (ETB), and community and comprehensive) and all schools follow the same curriculum and qualifications framework. Secondary education consists of the three-year junior cycle, followed by either two or three years of senior cycle, depending on whether a student participates in an optional transition year between the junior and the senior cycles (NCCA 2021).
There are 3 107 primary schools, 134 special schools that cater for students aged 5-18, and 730 post-primary schools, all of which follow the state curricula.19 In Ireland, the National Council for Curriculum and Assessment (NCCA), which is a statutory body of the Department of Education advises the Minister for Education on curriculum and assessment for early childhood education, primary and post-primary schools and assessment procedures used in schools and examinations on subjects which are part of the curriculum. This advice is developed through research, deliberation, consultation and networks.*
For more information on the national education system in Ireland, please visit:
*OHTE Thematic report on "Pandemics and natural disasters as reflected in history teaching"
HISTORY IN SCHOOL
Data are currently being collected for the OHTE general report.
This section will host information on the space and time provided to ‘History’ as a subject matter within the three main levels of education (primary, lower secondary and upper secondary). It will also provide insights on the relationship between history and other school subjects.
HISTORY CURRICULUM
Data are currently being collected for the OHTE general report.
Students study history as a discrete subject at primary and secondary levels. History is a compulsory subject until the third year of the junior cycle (ages 15-16) and is optional in the senior cycle (ages 17-18). There is a great degree of flexibility for teachers in how the history curriculum is delivered. A variety of teaching materials are used in the teaching of these subjects, including textbooks, worksheets, video and audio clips, digital material, documents, images, digital archives and other types of primary sources. The decision on which particular resources are used is a decision for individual schools. There are no requirements placed on a school by the Department of Education to use any specific textbooks. However, the department does provide advice and support through the National Council for Curriculum and Assessment (NCCA) and the department’s teacher support services. It also issues guidelines for teachers and provides support materials to help and guide their work with students.
Across all levels, the history curricula aim to develop an awareness of the discipline of history in students. Both the primary and junior cycle curricula pay attention to the development of the skills and dispositions needed to engage in historical research and to work with historical documents (“Working as a historian” at primary level and “The nature of history” at junior cycle level). This allows for progression to more detailed interrogation of the past at senior level. Historical enquiry is the recommended teaching pedagogy at all levels.*
Curricula workstation by GEI (History curricula search by country)
The National Council for Curriculum and Assessment (NCCA)
*OHTE Thematic report on "Pandemics and natural disasters as reflected in history teaching"
LEARNING OUTCOMES AND ASSESSMENT
Data are currently being collected for the OHTE general report.
This section will contain information on the learning outcomes set for history lessons within the different levels of education and on the methods of testing and assessment used in history examinations.
The National Council for Curriculum and Assessment (NCCA)
The State Examinations Commission (responsible for the development, assessment, accreditation and certification for the secondary level)
EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES AND PEDAGOGY USED IN THE HISTORY CLASSROOM
Data are currently being collected for the OHTE general report.
This section will host data on the study material and teaching practices used for history teaching within the different levels of education.
International TextbookCat (GEI collection of Textbooks and Educational Media)
HISTORY TEACHERS
Data are currently being collected for the OHTE general report.
This section will provide an overview of the number of history teachers within the different levels of education, as well as relevant information on teachers’ initial training and in-service training available to them.
History Teachers’ Association of Ireland (presentation by EuroClio)
History Teachers’ Association of Ireland (official website)
THEMATIC DATA
The Observatory on History Teaching in Europe also provides thematic studies on given topics.
2022: Pandemics and natural disasters as reflected in history teaching



